Beriberi: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Beriberi is a health condition caused by a deficiency of thiamine, also known as vitamin B1. This essential nutrient plays a crucial role in the body’s metabolism and nerve function. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures for beriberi is vital to maintaining optimal health. In this article, we will delve into the details of this condition and explore ways to safeguard against it.
Causes of Beriberi
Beriberi arises from a lack of thiamine in the diet, which is commonly found in foods such as whole grains, legumes, nuts, and pork. Several factors contribute to the development of thiamine deficiency:

- Poor Diet: Consuming an unbalanced diet lacking in essential vitamins and minerals, including thiamine, can lead to beriberi.
- Alcoholism: Excessive alcohol consumption interferes with the absorption and utilization of thiamine, increasing the risk of beriberi.
- Gut Disorders: Certain gastrointestinal disorders can impair thiamine absorption, reducing the body’s ability to utilize this vital nutrient effectively.
Symptoms of Beriberi
Recognizing the symptoms of beribery is crucial for early detection and intervention. The signs can vary depending on the type of beriberi, but common manifestations include:
1.Wet Beriberi:

Characterized by cardiovascular symptoms, such as swelling of the legs, shortness of breath, and an increased heart rate. Wet beriberi is a form of thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency that primarily affects the cardiovascular system. Thiamine is an essential nutrient required for the proper functioning of various enzymes involved in energy production.
2. Dry Beriberi:

This type primarily affects the nervous system, leading to muscle weakness, tingling or numbness in the extremities, and difficulty walking. Dry Beriberi can result in severe muscle wasting, making the affected muscles appear thin and flaccid. The weakness can become so profound that individuals may struggle to stand or bear weight on their legs, leading to difficulty walking or even complete immobility.
3.Infantile Beriberi:
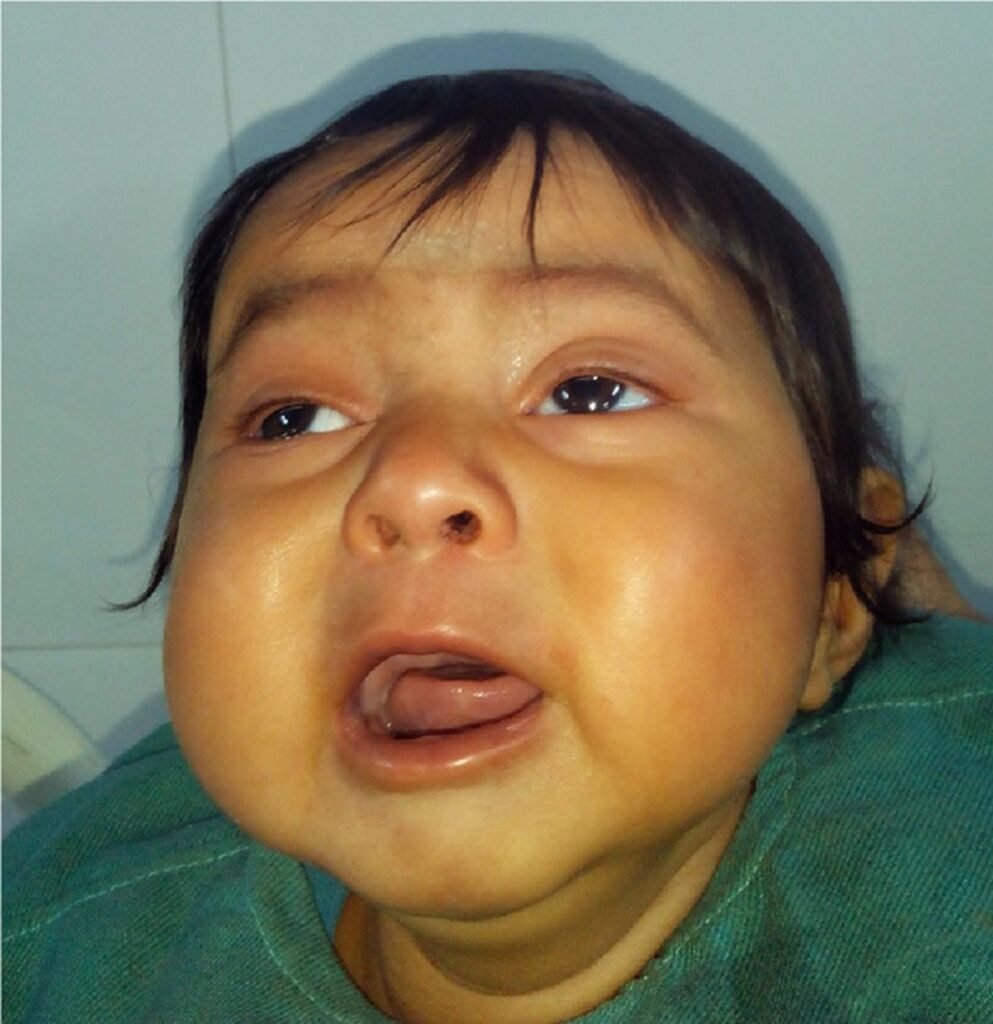
Infants with thiamine deficiency may experience irritability, muscle weakness, and feeding difficulties. Infantile Beriberi is a severe form of thiamine deficiency that primarily affects infants who are breastfed by thiamine-deficient mothers or are fed with thiamine-deficient formulas. This condition can have devastating effects on the developing nervous system of the infant.
Prevention of Beriberi
Preventing beriberi involves maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet to ensure an adequate intake of thiamine. Here are essential preventive measures:

- Healthy Diet: Incorporate thiamine-rich foods into your daily meals, such as whole grains, brown rice, legumes, nuts, and lean pork.
- Alcohol Moderation: If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation to minimize the risk of thiamine depletion.
- Thiamine Supplements: In cases where dietary intake is insufficient, consider thiamine supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Awareness and Education: Spread awareness about the importance of thiamine in overall health and the risks of deficiency through educational initiatives.
Conclusion
Beriberi, caused by thiamine deficiency, is a condition that can significantly impact an individual’s health if left untreated. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing preventive measures, you can safeguard yourself and your loved ones from this nutritional deficiency disorder. Ensure a balanced diet with thiamine-rich foods, moderate alcohol consumption, and consider supplements if necessary to maintain optimal health and well-being.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 99150 72372, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000