Can Fatty Liver Disease Increase Heart Disease Risk?
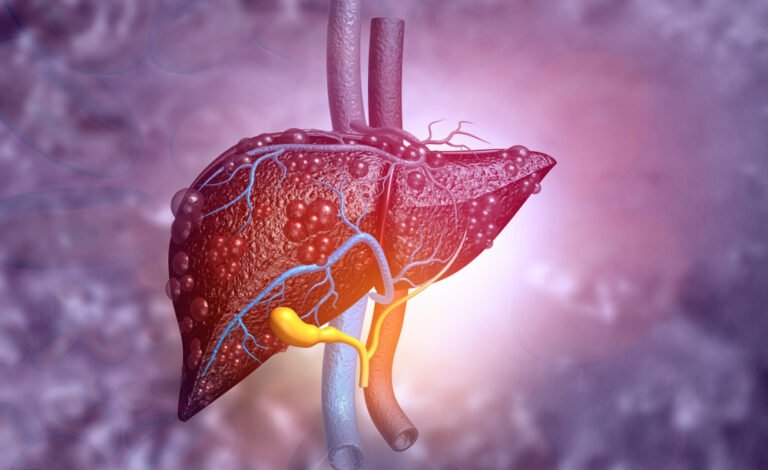
Fatty liver disease is a growing health concern worldwide, affecting millions due to poor lifestyle habits, unhealthy diets, and lack of physical activity. While it is primarily associated with liver complications, recent studies indicate that it may also increase the risk of heart disease. But is there a direct link between fatty liver disease and cardiovascular issues? Let’s explore expert insights and scientific findings.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease
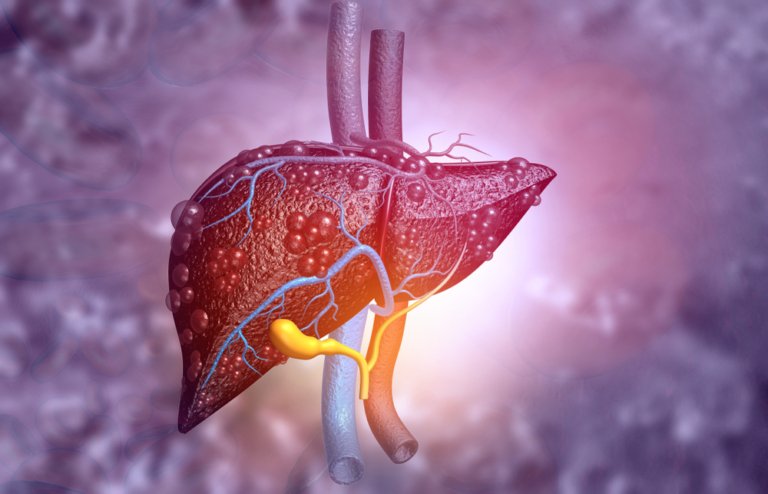
Fatty liver disease occurs when excess fat builds up in the liver. There are two main types: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), which is caused by obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic disorders, and Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD), which develops due to excessive alcohol consumption. Both types can progress to severe conditions such as cirrhosis, liver failure, or hepatocellular carcinoma.
The Connection Between Fatty Liver and Heart Disease
1. Impact on Cholesterol Levels
Fatty liver disease can lead to an imbalance in cholesterol levels. It often causes an increase in LDL (bad cholesterol) and a decrease in HDL (good cholesterol). This imbalance results in plaque buildup in the arteries, which increases the risk of heart disease.
2. Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome
People with fatty liver disease are more likely to develop insulin resistance. This condition contributes to metabolic syndrome, which includes high blood sugar, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels. These factors together significantly raise the risk of heart disease.
3. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress

Fatty liver disease triggers inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. These conditions damage blood vessels and make arteries more prone to atherosclerosis, which is the hardening and narrowing of the arteries. This increases the chances of heart attacks and strokes.
4. Hypertension and Arterial Stiffness
Many people with fatty liver disease also suffer from high blood pressure. The liver plays a role in regulating blood pressure, and when it is compromised, it can lead to arterial stiffness. This increases strain on the heart, raising the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
5. Liver Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Health
A damaged liver affects lipid metabolism, leading to higher triglyceride levels in the blood. Elevated triglycerides contribute to an increased risk of heart disease, as they can cause fatty deposits in arteries and lead to blockages.
How to Reduce the Risk of Heart Disease if You Have Fatty Liver
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet

Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential. Reducing the intake of saturated fats, processed foods, and refined sugars can help manage both liver and heart health.
2. Exercise Regularly

Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week can significantly improve liver function and heart health. Activities like walking, jogging, and strength training are beneficial.
3. Manage Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure

Monitoring and controlling blood sugar levels is crucial for those with fatty liver. Reducing sodium intake and maintaining a healthy weight can also help in managing blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease.
4. Avoid Alcohol and Smoking

Alcohol can worsen liver damage, and smoking contributes to inflammation and arterial blockage. Avoiding these habits can help improve overall cardiovascular health and prevent further complications.
5. Regular Health Check-Ups

Routine liver function tests and lipid profile check-ups are essential for early detection and management. Monitoring cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and liver enzymes can help in preventing complications related to both fatty liver and heart disease.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is not just a liver problem; it is closely linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Managing liver health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle changes can significantly lower the risk of cardiovascular issues. If you have fatty liver disease, taking proactive steps to protect your heart is crucial for overall well-being.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 99150 72372, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000