Unveiling the Effects of Sugar on Health and Well-being

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Sugar? Understanding the Effects of Sugar on the Body
In today’s fast-paced world, sugar has become more than just a sweet treat. It’s a staple in many diets, often hidden in foods we wouldn’t suspect. But what really happens to your body when you indulge in sugary delights? In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll dive deep into the effects of sugar on the body, shedding light on both the immediate and long-term impacts of this ubiquitous ingredient. Discover the surprising effects of sugar on health, from immediate energy spikes and crashes to long-term risks like obesity and diabetes.

1.Immediate Effects of Sugar Consumption
When you eat sugar, your body responds almost immediately. Sugar, particularly in its refined form, enters the bloodstream quickly, leading to a rapid spike in blood glucose levels. This spike prompts the pancreas to release insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose for energy.
The Sugar High and Crash
This process can lead to the well-known “sugar high,” characterized by a brief surge in energy and mood. However, this is often followed by the infamous “sugar crash,” a sudden drop in energy levels and mood, leaving you feeling tired and irritable. This cycle can affect your day-to-day productivity and overall well-being.

2.Long-Term Health Implications
While the occasional sugar treat is unlikely to cause long-term harm, consistent high sugar intake can lead to more serious health issues:
1.Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
High sugar consumption is a major contributor to obesity, a condition that can lead to a host of other health problems, including metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions, including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels, which together increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.
2.Diabetes
One of the most well-documented effects of long-term high sugar consumption is an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. As the body becomes overwhelmed by the frequent demands to process sugar, the effectiveness of insulin can diminish, leading to insulin resistance and eventually diabetes.
3.Dental Health
Sugar’s impact on dental health is also significant. It is a leading cause of dental decay and cavities. When sugar is consumed, it interacts with bacteria in the mouth to produce acid that can erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities.
3.Sugar and Mental Health
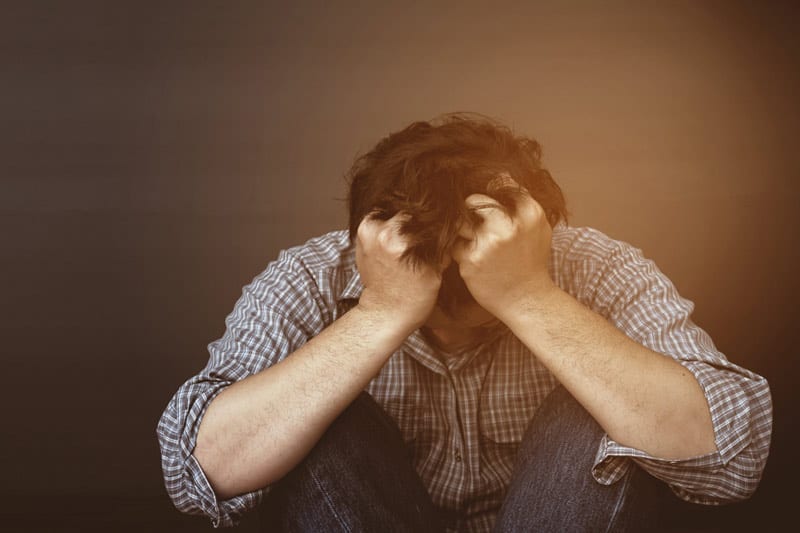

Emerging research suggests that high sugar intake may not only affect the body but also the mind. Diets high in sugar have been linked to an increased risk of depression and anxiety. The fluctuations in blood sugar levels can influence mood and mental health, contributing to mood swings and potentially exacerbating symptoms of mental health disorders.
4.Understanding Natural vs. Added Sugars
It’s important to distinguish between natural sugars, found in fruits and vegetables, and added sugars, found in processed foods. Natural sugars come with essential nutrients, fiber, and water, which help mitigate the negative effects of sugar on the body. In contrast, added sugars provide no nutritional value and pose a greater risk to health.
5.Tips for Reducing Sugar Intake
Reducing sugar intake can seem daunting, but with a few simple strategies, it’s entirely achievable:
- Read food labels carefully to identify added sugars.
- Opt for whole foods, like fruits and vegetables, over processed options.
- Satisfy sweet cravings with natural sugars from fruits or dark chocolate.
- Limit sugary beverages, opting for water, herbal teas, or unsweetened drinks instead
Conclusion
The effects of sugar on the body are profound and far-reaching, from immediate energy fluctuations to long-term health risks. By understanding these impacts and taking steps to moderate sugar intake, we can protect our health and improve our quality of life.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 99150 72372, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000