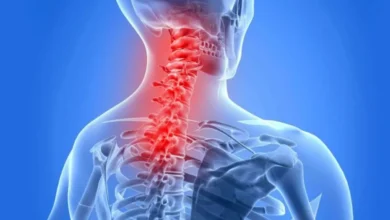
Thyroid Disease : Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment

Thyroid disease affects millions worldwide, presenting a significant health concern that spans various demographics. The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of your neck, plays a pivotal role in regulating numerous metabolic processes throughout the body. Given its critical functions, disorders of the thyroid can lead to widespread health issues, impacting overall well-being and quality of life.
What is Thyroid Disease?

Thyroid disease encompasses several types of conditions that can affect the thyroid gland’s function. The most common are hypothyroidism, where the gland underproduces thyroid hormones, and hyperthyroidism, characterized by an overproduction. Other conditions include thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid) and thyroid cancer. These disorders can have profound effects on the body’s energy levels, metabolism, and overall health.
Causes of Thyroid Disease
Thyroid diseases are a complex group of disorders that can significantly impact an individual’s health and quality of life. Understanding the root causes of these conditions is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Here, we delve into the various factors that contribute to the development of thyroid diseases.
1. Autoimmune Disorders
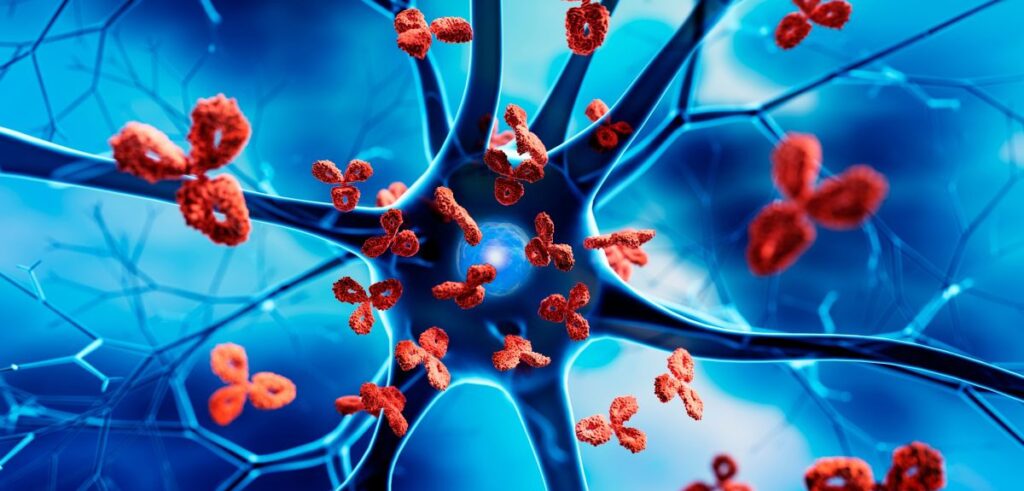
Autoimmune disorders are among the leading causes of thyroid diseases. In conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease, the body’s immune system mistakenly targets and damages the thyroid gland. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis often leads to hypothyroidism, where the thyroid underproduces hormones, while Graves’ disease typically results in hyperthyroidism, characterized by the overproduction of thyroid hormones.
2.Iodine Deficiency
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. A lack of iodine in the diet can lead to insufficient hormone production, resulting in hypothyroidism. This condition is more common in areas where iodine is scarce in the local diet. Conversely, excessive iodine intake can also cause thyroid dysfunction, underscoring the importance of a balanced iodine level.
3.Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in the predisposition to thyroid diseases. Family history of thyroid disorders increases the risk of developing similar conditions. Specific genetic mutations have been linked to various forms of thyroid disease, including congenital hypothyroidism and autoimmune thyroid conditions.
4.Environmental Toxins
Exposure to certain environmental toxins has been associated with an increased risk of thyroid disease. Substances such as radiation, pesticides, and certain chemicals can interfere with thyroid function and contribute to the development of thyroid disorders. For instance, radiation exposure, particularly in childhood, is a known risk factor for thyroid cancer.

Understanding the causes of thyroid disease is a crucial step toward effective management and treatment. By identifying the underlying factors, healthcare providers can tailor treatment strategies to address the specific needs of each individual, improving outcomes and enhancing quality of life.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disease

Symptoms of thyroid disease can be subtle and varied, often mimicking those of other conditions. Common signs include unexpected weight changes, mood swings, alterations in energy levels, and changes in heart rate. Those with hypothyroidism may experience fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance, whereas hyperthyroidism can cause weight loss, anxiety, heat intolerance, and palpitations.
Diagnosing Thyroid Disease
Diagnosing thyroid disease typically involves a combination of physical examinations, symptom assessment, and specific blood tests to measure levels of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) and thyroid hormones . Advanced diagnostic tools, such as thyroid ultrasound and scans, may also be employed to assess the gland’s size, shape, and the presence of nodules.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Disease
Treatment strategies for thyroid disease depend on the specific disorder and its severity. Hypothyroidism is commonly managed with hormone replacement therapy, while hyperthyroidism treatments may include medication, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery in severe cases. Lifestyle adjustments, such as dietary changes and stress management, can also play a crucial role in managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
Managing Thyroid Health
Regular monitoring and proactive management of thyroid health are essential for those diagnosed with or at risk for thyroid disease. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in iodine and selenium, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques can support thyroid function and mitigate disease symptoms. Importantly, ongoing communication with healthcare providers ensures that treatment plans remain effective and are adjusted as needed.
Conclusion
Thyroid disease, with its myriad causes and manifestations, represents a significant health challenge. Understanding its symptoms, engaging in regular health screenings, and adopting a proactive approach to treatment can significantly improve outcomes for those affected. As research continues to advance our understanding of thyroid disorders, there remains hope for more effective treatments and strategies for prevention in the future.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 99150 72372, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000