What is the best treatment for osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis, often dubbed the “silent thief,” gradually weakens bones without any visible symptoms until a fracture occurs. This bone condition affects millions worldwide, posing significant health risks and impacting the quality of life. Understanding osteoporosis’s underlying causes, recognizing its subtle symptoms, and exploring effective treatment options are pivotal steps towards proactive bone health management. Unlock the best treatment for osteoporosis From cutting-edge medications to lifestyle changes, learn how to boost bone health and reduce fracture risks effectively. Your guide to stronger bones starts here.
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone disease characterized by reduced bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to enhanced bone fragility and an increased risk of fractures. While it can affect anyone, postmenopausal women and the elderly are at a higher risk due to hormonal changes and age-related bone density loss. The condition is often undetected until a minor fall or sudden impact causes a bone fracture, highlighting the importance of early detection and prevention strategies.
Causes of Osteoporosis
Understanding the multifaceted causes of osteoporosis is essential for prevention and management:
- Genetic Factors: A family history of osteoporosis or fractures can significantly increase one’s risk.
- Hormonal Imbalances: For women, the drop in estrogen levels during menopause is a key risk factor. In men, reduced testosterone levels can lead to bone density loss.
- Insufficient Nutrition: A diet lacking in calcium and vitamin D plays a crucial role in bone health, as these nutrients are vital for bone density and strength.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and sedentary lifestyles contribute to weakening bones.
- Chronic Conditions and Medication: Certain medical conditions (such as rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid issues) and medications (like steroids) can accelerate bone loss.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
1.Back Pain
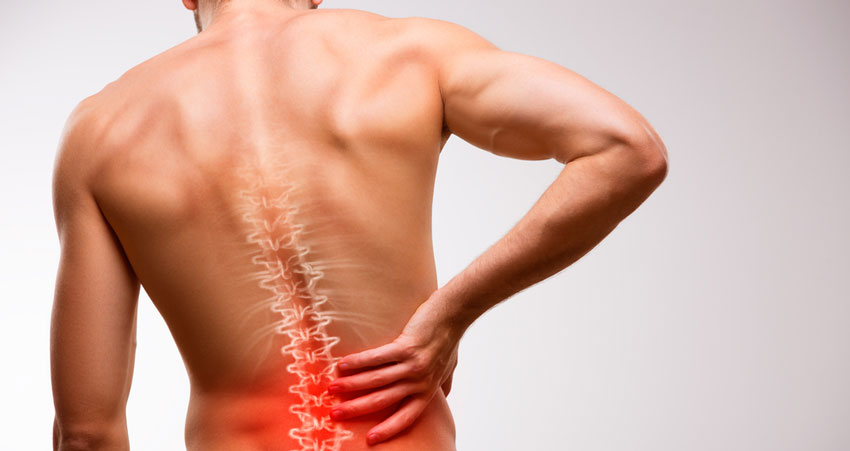
Often, the first indicator of osteoporosis is back pain, arising from fractures or collapsed vertebrae. This pain signifies changes within the spine, reflecting the weakening of bones. As the condition advances, these spinal changes become more pronounced, leading to chronic discomfort and potential mobility issues, emphasizing the importance of early detection and management of osteoporosis to prevent such complications.
2.Height Reduction

A subtle but noticeable reduction in height over time can be a telltale sign of osteoporosis. This height loss is typically due to the compression of the vertebrae in the spine, a direct result of weakened bone structure. Alongside height reduction, individuals may develop a stooped or hunched posture, known as kyphosis, which further indicates significant bone density loss and warrants immediate medical attention.
3.Fragile Bones
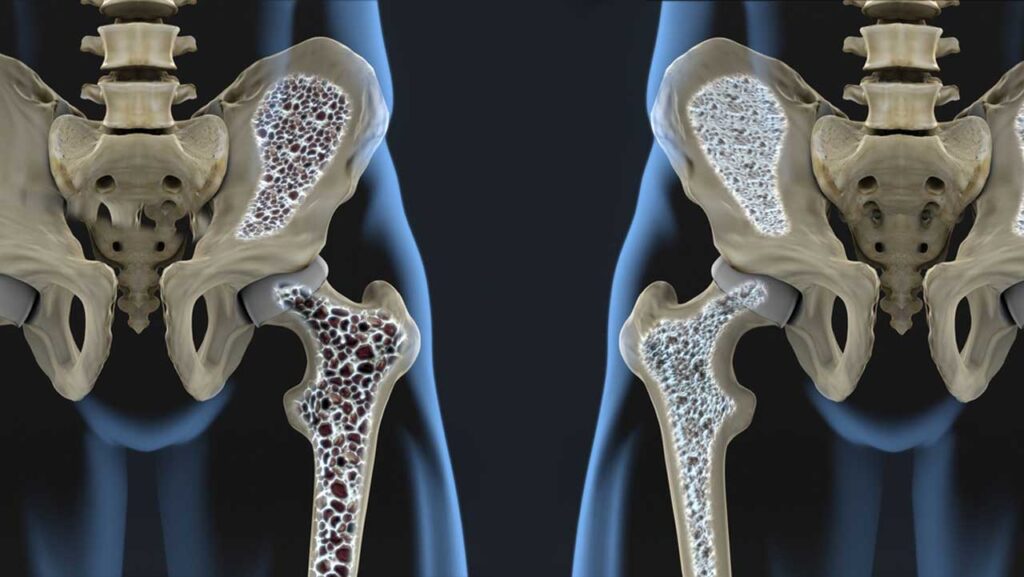
Osteoporosis significantly increases the risk of fractures from actions that would not typically cause injury, such as minor falls or even routine movements like bending or coughing. This heightened fracture risk is especially prevalent in the hips, wrists, and spine, areas most vulnerable to the effects of bone density loss. The occurrence of these fractures often serves as a wake-up call, highlighting the silent progression of osteoporosis and the need for proactive bone health management.
Diagnosis of Osteoporosis
Early diagnosis can significantly affect the management and outcome of osteoporosis:
- Bone Density Test (DEXA Scan): Measures the grams of calcium and other bone minerals, providing a snapshot of bone health.
- FRAX Score: A tool used to estimate the 10-year fracture risk based on individual patient models.
- Laboratory Tests: Assess for underlying conditions or vitamin deficiencies that could affect bone health.
Treatment and Management of Osteoporosis
Effective treatment and management strategies are tailored to individual risk factors and the severity of bone loss:
1.Medications
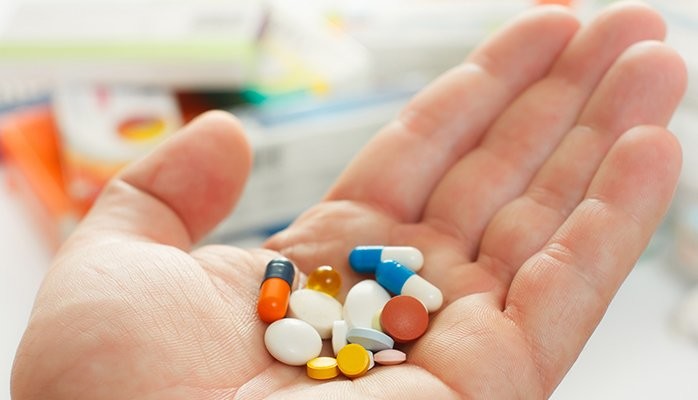

Bisphosphonates stand as the cornerstone of osteoporosis treatment, effectively slowing bone loss and reducing fracture risk. Alternatives like Denosumab and Teriparatide offer solutions for those who may not tolerate bisphosphonates well, targeting the bone remodeling process differently. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) can be beneficial, particularly for postmenopausal women, by addressing the estrogen deficiency that accelerates bone loss, though it comes with its own risk considerations.
2.Lifestyle Modifications
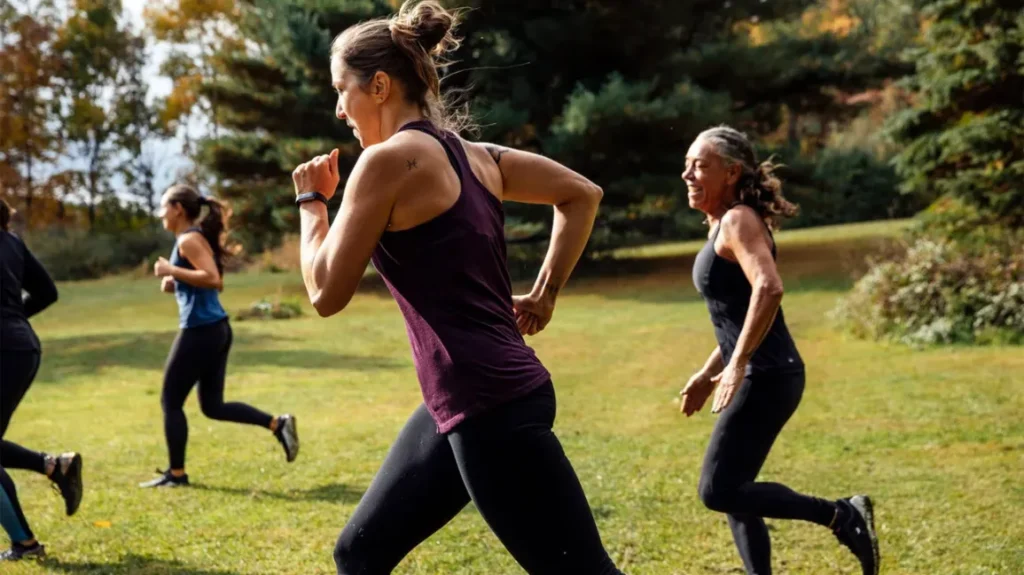
A holistic approach to managing osteoporosis includes significant lifestyle changes. A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D supports bone health, while regular weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises improve bone density and muscle strength, reducing the risk of falls and fractures. Additionally, quitting smoking and moderating alcohol consumption can have a profound impact on slowing bone density loss and enhancing overall health.
3.Fall Prevention
With fractures posing a significant risk, especially in advanced osteoporosis, fall prevention becomes a critical component of management. This involves assessing and modifying living environments to remove potential hazards, such as securing rugs and improving lighting. Use of assistive devices like canes or walkers for those with balance issues, alongside exercises aimed at improving balance and strength, can further mitigate the risk of falls, protecting against serious bone injuries.
Living with Osteoporosis
Living with osteoporosis doesn’t mean giving up an active lifestyle. It’s about making informed choices:
- Nutritional Guidance: Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D, either through diet or supplements, following a healthcare provider’s recommendations.
- Exercise Regularly: Tailor your exercise routine to include activities that strengthen bones and muscles without putting undue stress on them.
- Monitor Bone Health: Regular follow-up appointments and bone density tests can help track the effectiveness of treatment plans and adjust as necessary.
Conclusion
Osteoporosis poses significant challenges, but with informed strategies, it’s possible to manage the condition effectively and maintain a high quality of life. Early detection, lifestyle adjustments, and appropriate treatment plans are key. Encourage readers to engage with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized approach to osteoporosis management, ensuring stronger bones and a healthier future.
If you have any queries related to medical health, consult Subhash Goyal or his team members on this given no +91 99150 72372, +91 99150 99575, +918283060000