Effective Home Remedies for Relieving Cold Cough

Cold cough” is not a medical term but is commonly used to refer to the symptoms of a cold or the common cold, which can include coughing. A cold Cough, also known as the common cold, is a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract. It is usually caused by rhinoviruses and can lead to symptoms such as:
- Runny or Stuffy Nose
- Sneezing
- Sore Throat
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Watery Eyes , etc
Symptoms And Causes of a Cold Cough
1.Runny or Stuffy Nose:

The onset of a runny or stuffy nose is often one of the earliest signs of a common cold. In response to the viral infection, the nasal passages may become congested, leading to a feeling of stuffiness, making it difficult to breathe through the nose. Simultaneously, the body’s immune response may lead to the production of clear mucus, resulting in a runny nose. This combination of symptoms can make breathing uncomfortable and hinder the sense of smell.
2. Sneezing:

Frequent sneezing is a hallmark of a cold, particularly in its initial stages. The body’s reflex response to the presence of cold viruses in the nasal passages or throat often results in repeated sneezing. This action is an attempt to expel the irritants and viruses from the respiratory system.
3. Sore Throat:

A scratchy or sore throat is a common complaint during a cold. It can manifest as an early symptom or develop as the cold progresses. The viral infection can lead to inflammation and irritation of the throat tissues, causing discomfort and a sensation of scratchiness or soreness. This symptom can make swallowing and speaking painful.
4.Cough:
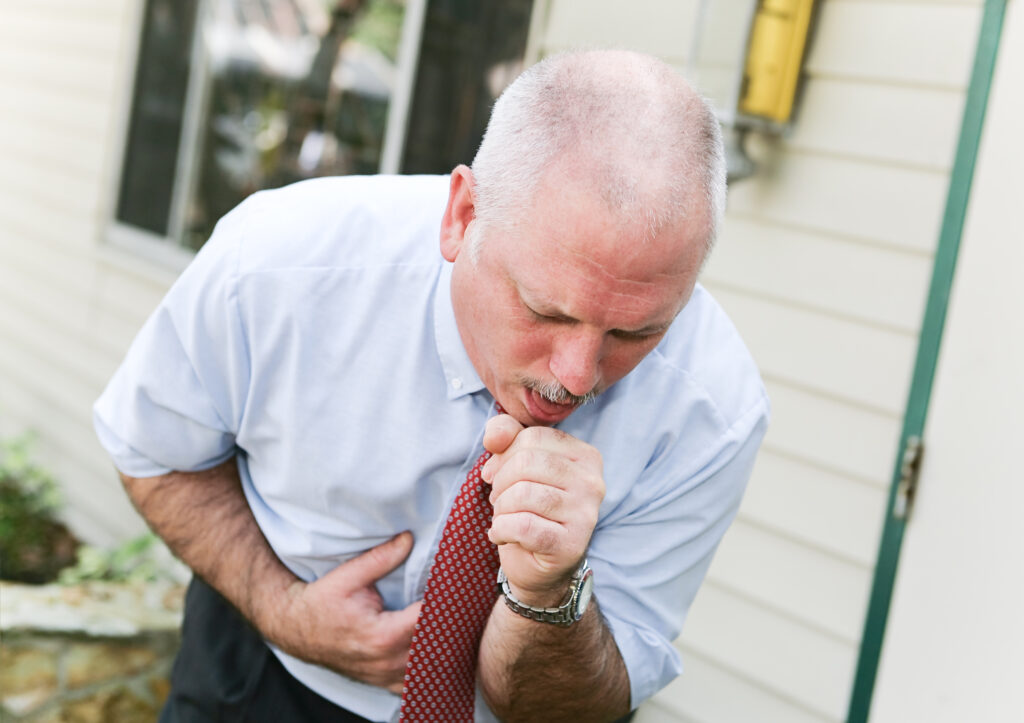

Coughing is a prevalent symptom of a cold, and it serves as the body’s natural mechanism to clear the airways of excess mucus and irritants. The nature of the cough can vary; it may be dry and hacking or productive, producing mucus. This reflexive response can persist as the body attempts to rid itself of viral particles and mucus buildup.
5. Fatigue:
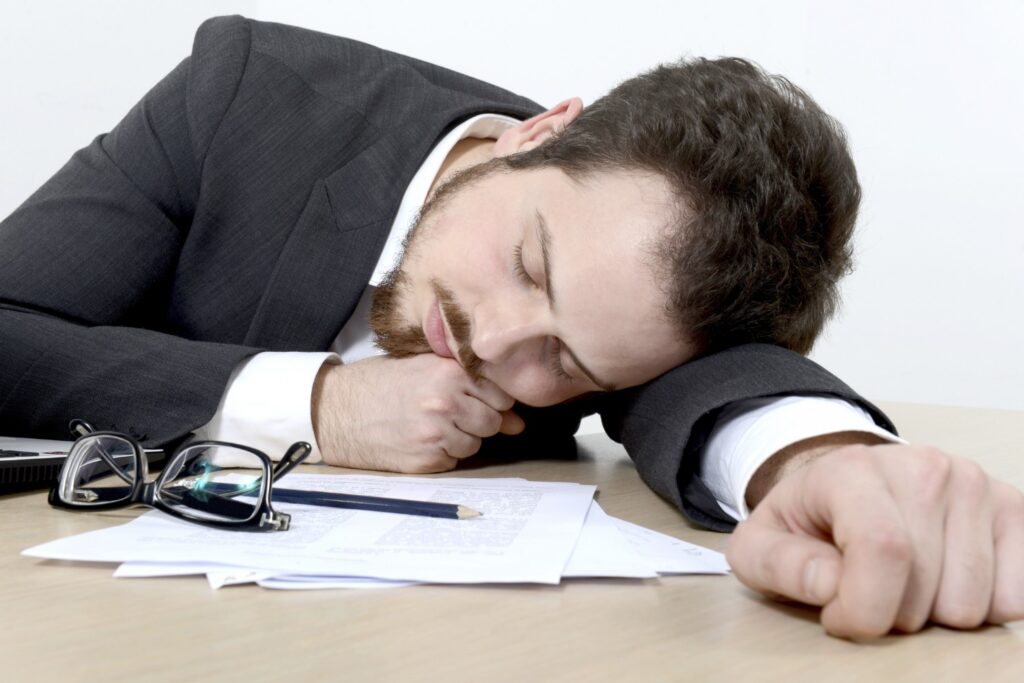

A common cold can leave individuals feeling drained of energy and fatigued. This fatigue is often a result of the body’s immune system working tirelessly to combat the viral infection. Additionally, disrupted sleep due to congestion, coughing, or discomfort can contribute to this feeling of tiredness.
6. Watery Eyes:

Cold symptoms can extend to the eyes, causing them to become watery or itchy. This ocular discomfort can result from the body’s inflammatory response to the virus or from the drainage of excess mucus from the nasal passages into the tear ducts.
7. Mild Headache:

Many individuals experience mild headaches when they have a cold. These headaches are often attributed to the overall inflammation and congestion in the head and sinus areas. The discomfort can range from a dull ache to a mild throbbing sensation.
8. Mild Fever:

While a low-grade fever is possible during a cold, it is not always present. Fever is a part of the body’s defense mechanism against infection. It may manifest as a slightly elevated body temperature as the immune system responds to the invading virus. However, the fever associated with a cold is typically mild and transient.
9. Body Aches:
Some people with colds may experience mild body aches and discomfort. These aches are generally the result of the body’s inflammatory response to the viral infection. They can affect various muscle groups, causing a general sense of bodily discomfort and soreness.
10.Slight Chest Discomfort:
In some cases, individuals with a cold may feel mild discomfort or tightness in the chest, particularly when coughing. This sensation can arise as a secondary effect of persistent coughing, as the muscles used during coughing may become fatigued or strained. It’s essential to differentiate this mild chest discomfort from more serious chest conditions, which require immediate medical attention.
Risk factors Of cold Cough

Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of contracting a common cold or experiencing more severe symptoms when infected. These risk factors include:
- Age: Children under the age of 6 are at a higher risk of contracting cold Cough because their immune systems are still developing and they may have less immunity to various viruses. Older adults may also be more susceptible to severe colds due to age-related changes in the immune system.
- Season: Colds are more common in the fall and winter months, as many cold-causing viruses thrive in colder, drier conditions.
- Weakened Immune System: People with compromised immune systems, such as individuals with HIV/AIDS, cancer, or autoimmune disorders, are at greater risk of contracting and experiencing severe colds.
- Exposure: Being in close contact with individuals who have colds, such as in crowded places, schools, or public transportation, increases the risk of transmission.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the respiratory system and weakens the immune system, making smokers more susceptible to colds and respiratory infections.
- Stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections like the common cold.
- Allergies: Individuals with allergies may have more frequent cold-like symptoms due to a heightened sensitivity of the nasal passages and airways.
- Poor Hygiene: Not practicing good hand hygiene, such as regular handwashing with soap and water, and touching one’s face, especially the nose and mouth, with contaminated hands can increase the risk of cold transmission.
- Lack of Sleep: Inadequate sleep can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections like the common cold.