Lung Cancer: Types, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Lung cancer is a condition where cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that can impair breathing and spread to other body parts. It’s a major health concern worldwide due to its high mortality rate. Dive into our comprehensive guide on lung cancer, covering everything from its types (NSCLC and SCLC) to early signs, causes, and innovative treatments.
1.Types of Lung Cancer
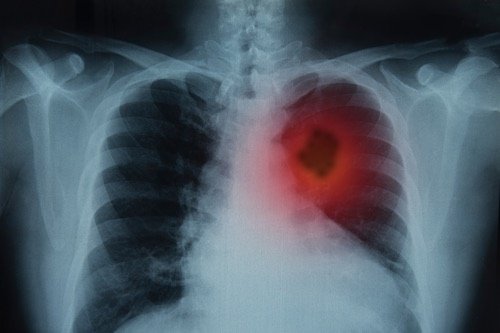
1. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
NSCLC, the most common lung cancer type, grows more slowly than SCLC. Its subtypes, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma, vary in their location within the lung and how quickly they spread. Treatment and prognosis differ by subtype, making accurate diagnosis vital.
2. Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
SCLC is aggressive and fast-spreading, often diagnosed at an advanced stage due to its rapid growth. It is primarily associated with heavy smoking and requires immediate and intensive treatment, including chemotherapy and radiation, to manage its swift progression.
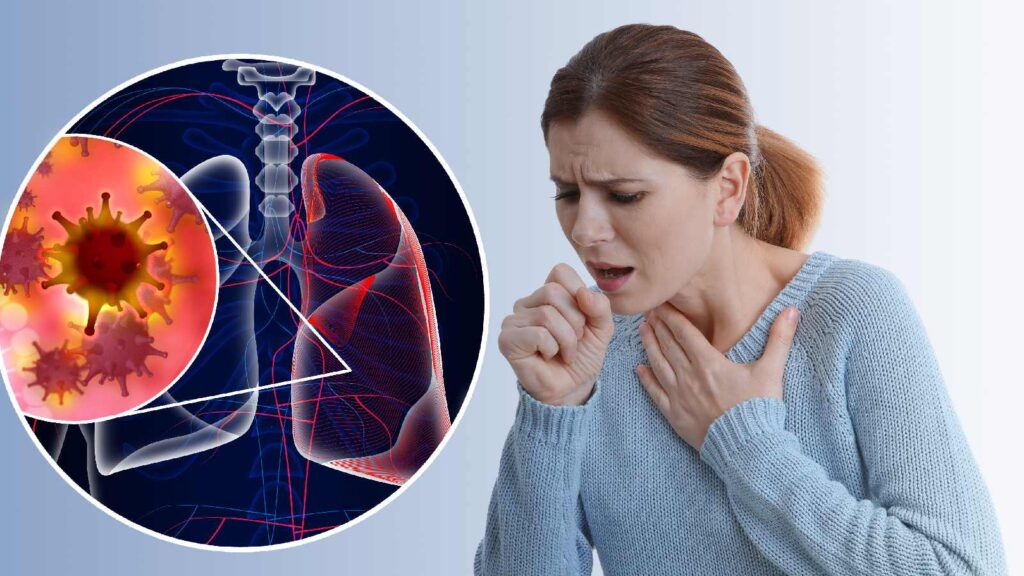
2. Signs of Lung Cancer

Lung cancer symptoms often appear only after the disease has advanced, making early detection challenging. Recognizing early signs, such as a persistent cough, breathlessness, and chest pain, can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment. Regular health check-ups and attention to lung health are essential, especially for smokers and those exposed to lung cancer risk factors.
3. Causes of Lung Cancer
1.Smoking and Tobacco Use

The link between smoking and lung cancer is well-established, with smoking being the primary cause of the disease. Quitting smoking at any age can significantly reduce the risk, emphasizing the importance of cessation programs and education in preventing lung cancer.
2. Other Risk Factors
Beyond smoking, exposure to radon, asbestos, and other carcinogens can increase lung cancer risk. Genetic factors and a family history of the disease also contribute, underscoring the need for risk awareness and preventive measures in at-risk populations.
3. Diagnosing Lung Cancer

Early diagnosis of lung cancer can be challenging due to its subtle symptoms. Modern diagnostic tools, including advanced imaging techniques and minimally invasive procedures for biopsy, are essential for accurate diagnosis. Early and accurate diagnosis improves the chances of successful treatment, highlighting the importance of regular screenings for high-risk individuals.
4.Treating Lung Cancer
The treatment of lung cancer has evolved, with options now including minimally invasive surgery, precision radiation therapy, and innovative drugs targeting specific genetic mutations in cancer cells. These advancements offer hope for improved survival rates and quality of life for patients, emphasizing the importance of personalized treatment plans.
4. Preventing Lung Cancer
1.Reducing Exposure to Risk Factors
Prevention strategies focus on reducing exposure to known risk factors, particularly smoking. Public health initiatives aimed at smoking cessation, reducing radon exposure, and limiting contact with carcinogens are critical in the fight against lung cancer. Healthy lifestyle choices, including diet and exercise, also play a role in prevention.
2. Living with Lung Cancer
The journey of living with lung cancer involves not only medical treatment but also emotional and psychological support. Resources such as support groups, counseling, and comprehensive care teams are invaluable for patients and their families, helping them navigate the challenges of the disease and treatment processes.