Thyroid Disease in Women: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
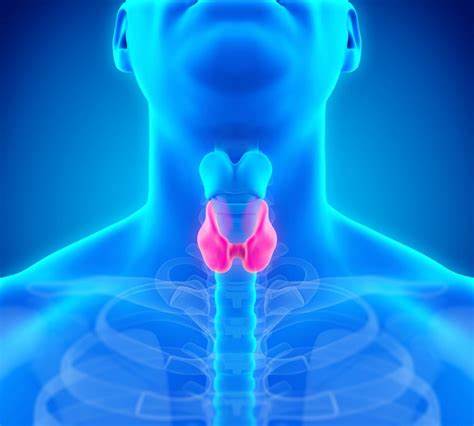
Thyroid disease in women is a condition that affects the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck. It plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and producing hormones that control various bodily functions. Thyroid disease is more common in women, and it encompasses different disorders such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid nodules. These conditions can lead to a range of symptoms including fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and irregular menstrual cycles. It is important for women to be aware of the signs and symptoms of thyroid disease and seek proper medical attention for diagnosis and treatment to maintain optimal thyroid health.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disease in Women
1. Fatigue:

Persistent fatigue or exhaustion, even after getting enough sleep, is a common symptom. Thyroid Disease in Women may feel constantly drained of energy.
2. Weight Changes:

Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight despite maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine can be a symptom of an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism). Conversely, unexpected weight loss can be a sign of an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism).
3. Mood Swings:
Thyroid imbalances can affect mood stability, leading to irritability, anxiety, depression, or sudden mood swings.
4. Hair and Skin Changes:

Brittle hair, hair loss (especially from the outer edge of eyebrows), dry skin, and brittle nails can indicate thyroid dysfunction.
5. Menstrual Irregularities:
Women with thyroid disease may experience changes in their menstrual cycle. It can range from heavy or irregular periods to shorter or longer cycles.
6. Muscle and Joint Discomfort:

Muscle weakness, aches, and joint pain are common symptoms. Women may experience stiffness or swelling in their joints.
7. Cold Sensitivity:
Feeling excessively cold, particularly in the hands and feet, can be a sign of an underactive thyroid.
8. Digestive Issues:

Some women with thyroid disease may experience constipation, bloating, or other digestive problems.
9. thyroid disease
Thyroid disease refers to disorders that affect the thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the neck. It can encompass conditions such as hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and thyroid nodules. Thyroid disease is more prevalent in women, and it can disrupt the normal functioning of the thyroid, leading to various symptoms and health complications. Women with thyroid disease may experience issues with metabolism, weight management, energy levels, mood, menstrual cycles, hair and skin health, and other bodily functions. It is crucial for women to be aware of the signs and symptoms of thyroid disease and seek medical attention for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
treatment Of Thyroid
1. Medication:

Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is the standard treatment for hypothyroidism, where synthetic thyroid hormones are prescribed to compensate for the underproduction of hormones. Anti-thyroid medications are used to control the excessive production of hormones in hyperthyroidism.
2. Radioactive Iodine Therapy:
This treatment option is primarily used for hyperthyroidism. Radioactive iodine is taken orally, and it helps destroy the overactive thyroid cells. It may result in hypothyroidism, which is then managed with hormone replacement therapy.
3. Surgery:
In Case Thyroid Disease in Women where medication or radioactive iodine therapy is not suitable or effective, surgery may be recommended. Surgical removal of all or part of the thyroid gland, known as a thyroidectomy, may be necessary for conditions such as thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer.
4. Lifestyle Modifications:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can be beneficial in managing thyroid disease. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and adequate sleep.
5. Regular Monitoring:
Women with thyroid disease often require ongoing monitoring through regular check-ups and blood tests to assess hormone levels and adjust medication dosage if needed.